The sulphur hexafluoride gas (SF6) is used as an arc quenching medium in Circuit breakers, which is called as SF6 circuit breaker. Sulphur hexafluoride gas (SF6) has a strong tendency to absorb the free electrons, because it is an electronegative gas. SF6 circuit breakers are mostly use in high power and high voltage applications.
Table of Contents
ToggleConstruction of SF6 circuit breaker
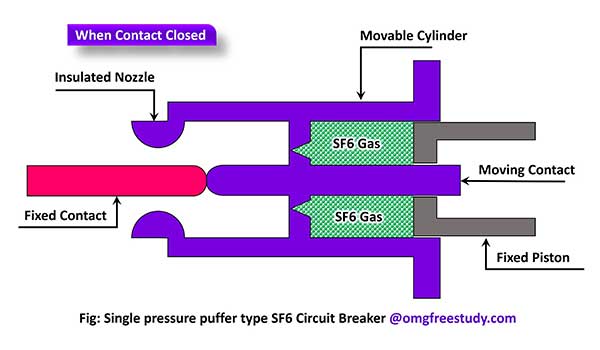
SF6 circuit breaker consists of two contact fixed and moving contacts which is enclosed in a cylindrical shape chamber. Figure shows typical sectional view of single puffer type SF6 circuit breaker.
The cylindrical chamber is called arc interruption chamber, which contains the SF6 gas. This chamber is divided in to two part, which one contain sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) gas reservoir and another as hollow cylinder as arc interruption chamber.
A valve system is present inside movable cylinder to permit the gas to the arc interruption chamber.
When circuit breaker contacts are opened, the valve mechanism open for high-pressure sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) gas from the reservoir to flow towards the arc interruption chamber.
The fixed contact is a hollow cylinder current carrying contact fitted with an arcing horn. The moving contact is also a hollow cylinder with rectangular holes in sides it.
Arc-resistant material are coated with a copper-tungsten on tips of fixed contact, moving contact and arcing horn to avoid carbon deposits on contact tips.
Working of SF6 circuit breaker
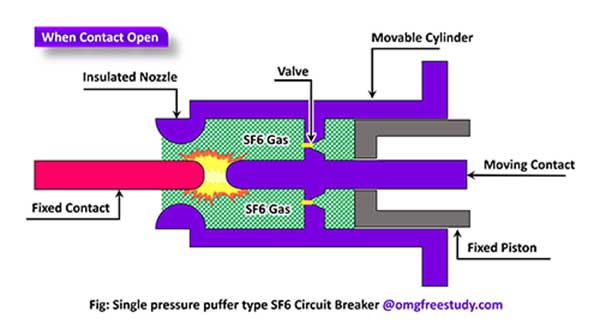
In the closed position of the breaker, the contacts surrounded by SF6 Gas is compressed at a pressure of about 2.8 kg/cm2.
When the breaker contacts opens, the moving contact is pulled apart and an arc is struck between the contacts.
The movement of the moving cylinder move contact with the opening of a valve. Which permits SF6 gas at 14kg /cm2 pressure from the reservoir to rapidly absorb the free electrons to form immovable negative ions which are ineffective as charge carriers.
The result is that improve the dielectric strength and causes the extinction of the arc.
Stepwise Operation of SF6 Circuit breaker:
- Fixed contact and moving contact are closed.
- When contact open, Arc struck between fixed and moving contact.
- Movable cylinder move away from fixed contact.
- Fixed piston exerted pressure on gas.
- Pressurized SF6 gas move toward arc struck, through valve.
- Then extinction of the arc.
Properties of SF6 gas
- Stable at high temperature around 500 0 C.
- Inert gas.
- Electronegative gas.
- Non-reactive with structured material up to 500 0 C.
- Low arc time constant.
- Five times heavier compared to air.
- Very much better dielectric properties compared to air and oil.
- Higher rate of rise of dielectric strength.
- The products of decomposed gas at high temperatures recombine on cooling to form original gas.
- For equal pressure the heat transfer capacity is more than twice of air.
- Non-toxic gas.
- Non-flammable gas.
- The SF6 ions surround the arc and form an insulating barrier.
Advantage of SF6 circuit breaker
- Since the dielectric strength of SF6 gas is 2 to 3 times more than the air.
- SF6 circuit breaker gives noiseless operation.
- Due to superior arc quenching property, they have very short arcing time.
- As SF6 gas is non-inflammable, no risk of fire.
- Noiseless operation.
- It does not pollute the atmosphere.
- Very much suitable in coal mines etc.
- They have minimum maintenance cost.
- The same gas is recycled and reused.
- There are no carbon deposits on contact tips.
- It is very much suitable for high voltage applications.
- Because of very high dielectric strength, effective arc quenching is possible.
Disadvantages of SF6 CB:
- SF6 gas is very costly. Hence this CB is expensive
- SF6 gas has to be reconditioned after every operation.
Assignment:
Que. Explain construction and working of SF6 circuit breaker
Que. Give any four properties of SF6 gas.
Que. Give any two advantages and two disadvantages of SF6 CB.
MCQ Questions PDF of Module 13 : Circuit Breakers and Relays
- Line protective relays – types – operation
- Circuit breakers – parts – functions- tripping mechanism
- Tripping mechanism of circuit breakers
- Repair and maintenance of CBs
Download MCQ Questions PDF of Circuit Breakers and Relays